No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

If you go through food labels, you must have come across maltodextrin in the ingredient list. It is a commonly used ingredient in processed packaged foods. Maltodextrin has several applications in the food industry, has some health benefits but it has also been associated with many health risks. In this article, we have summarised the applications of maltodextrin, its benefits, its impact on health, alternatives, and identification of maltodextrin and substitutes in the packaged foods using food labels.
Richa Pande
Maltodextrin is produced from corn starch, rice starch, potato starch, or wheat starch after undergoing extensive processing. It is added in the food products to increase their caloric content, improve food palatability, and to maintain the food quality. It is also commonly used as a thickening and stabilizing agent. Maltodextrin is also used as a preservative that increases the shelf life of packaged foods. It is often used in preparation of fast foods and packaged snacks. It is also used to replacing sugar or fat in processed foods. Maltodextrin is also used as a filler in production of many food items and nutrition supplements. It is also used as a binding and carrier agent in production of tablets and capsules, and many sports supplements.
Maltodextrin is a FDA approved food ingredient. Maltodextrin has a high glycaemic index (GI) value. In fact, maltodextrin’s GI higher than that of table sugar. This means that maltodextrin can cause a spike in your blood sugar levels even quicker than table sugar. This is the reason why we should limit the consumption of foods containing maltodextrin as it is always recommended to have foods with low GI. Foods with high GI should be specifically avoided by diabetics. Some research studies suggest that maltodextrin is also not good for the gut health. It has been found that maltodextrin can increase the growth of bacteria such as E. coli, which increases the risk of development of autoimmune diseases, and increase the risk of colitis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Some people can experience allergic reactions after consumption of maltodextrin. This includes gas, borborygmus, diarrhoea, cramping and skin irritations. However, some research work also suggests that maltodextrin can promote the growth of Bifidobacterium in the gut, which is good for gut health. It is also well-known for its laxative properties. Some studies have even found that maltodextrin can be helpful in the prevention of colorectal cancer.
Some healthier alternatives of maltodextrin are-Pectin, Stevia, Guar Gum, Sago, Sorbitol, Erythritol.
Maltodextrin is commonly found in these food products-
It is always recommended to go through the food labels to avoid picking food products that have maltodextrin in them. You can identify these products by going through the ingredient list and check if it has maltodextrin in it. You can also establish an understanding about the composition of maltodextrin in the food product. If it’s mentioned as the first ingredient in the ingredient list, then it means that the product is the major ingredient in that specific product. By referring to the ingredient list, you can establish an understanding if a product is healthy or not. Product 1 and product 2 below are oats and soup packs that are generally perceived as healthier products. By referring to the ingredient list, you can make an informed choice about the food product.

Pack one is a ready-to-eat oat snack, has maltodextrin in it.

Pack two is an instant soup powder that has maltodextrin in it.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Human gut is home to many species of microbes, collectively referred as ‘gut microbiota’. They can be both symbiotic and pathogenic in nature, coexisting together without causing any trouble. Sometimes this balance could be disturbed due to infectious illnesses, unhealthy diets patterns, prolonged use of antibiotics, sleep fragmentation and short sleep duration, etc. It can cause dysbiosis, stopping these normal interactions. Evidence suggests that the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in digestion and absorption of nutrients and thus impacting the health and nutrition status of an individual. In this article, we will discuss this in detail.
Richa Pande
In our body, digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place primarily in the stomach and small intestine. Gut microbes play a crucial role in digestion and absorption of macronutrients. They also play a critical role in fermentation of dietary fibre for the production of Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA), which are absorbed and utilized for different processes of the body. The gut microbiota is also important for synthesis of vitamin B12 in the colon, and facilitates the synthesis of nutrients such as thiamine, folate, biotin, riboflavin, and pantothenic acid. Gut microbes have been found be helpful in also helping us to meet our daily requirement of vitamin K. Gut microbiota is also linked with release of many gut hormones that controls our appetite and satiety levels thus impacting our weight status.
Several factors including diet, physical activity, genetics, drugs, caffeine, alcohol, and psychological status can play a role in influencing the gut microbiota. It further impacts the digestion, bioavailability, and absorption of the nutrients, thus impacting our health and nutrition status.
Imbalance in the gut bacteria is referred to as dysbiosis. It causes a variety of digestive disturbance symptoms, such as indigestion, bloating, cramps, diarrhoea, and constipation.
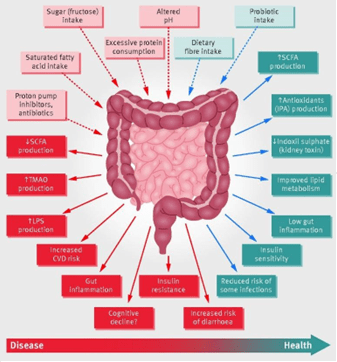
Source: Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health, Ana M Valdes et.al
Gut dysbiosis can be initially treated through medications and a healthy diet can help heal the gut to its normal stage and enable it to function normally. It takes at least a couple of weeks of healthy diet changes before gut dysbiosis is healed.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Eggs are one of nature’s most nutrient-dense foods. They are rich in essential micronutrients and provide high-quality protein. There are innumerable benefits of eating eggs regularly. Selection of eggs is simple, but presence of different varieties of eggs in the market and different health claims on egg cartons might confuse consumers. In this article, we talk all about how to choose quality eggs, and have also listed some tips that could help in safe handling of eggs.
Richa Pande
Eggs contain 13 essential vitamins and minerals and are a good source of protein of high biological values. Biological value refers to the proportion of absorbed protein from a food item which is incorporated into the proteins of the organism’s body. Eggs are one of the few dietary sources of vitamin D which has several health benefits. They are also a good source of biotin, which plays a vital role in assisting enzymes to break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins in food. They also contain antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin that help protect our body from free radicals.
|
Chemical Constituents In (%) |
Chicken | Turkey |
Guinea Fowl |
Quail | Duck | Goose |
| Water (%) | 72.8 -75.6 | 71.6-75.7 | 71.3-74.1 | 73.1-76.4 | 68.2-71.4 | 68.9-72.3 |
| Proteins (%) | 12.8 – 13.4 | 12.6-13.6 | 12.8-14.2 | 12.5-13.4 | 13.1-14.2 | 13.4-14.3 |
| Fats (%) | 10.5 – 11.8 | 10.8-12.6 | 11.2-12.8 | 10.6-11.7 | 13.8-15.0 | 12.4-13.6 |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 0.3 – 1.0 | 0.6-0.8 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.8-1.0 | 1.1-1.3 | 1.1-1.3 |
| Ash (%) | 0.8 – 1.0 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.7-0.1 | 1.0-1.2 | 0.9-1.0 | 1.0-1.4 |
Many health-conscious people discard egg yolk and prefer only the egg white portion of the egg as it is rich in proteins, and has very less amounts of fat and cholesterol. But it must be noted that fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A & D are present only in the egg yolk portion. The yolk also contains many essential B-Complex vitamins.
Egg yolk should be discarded due to the cholesterol content
A single egg contains about 180-200 mg of cholesterol which is over half of the recommended daily intake of 300 mg, and this is a concern for many health experts which is why they refrain from recommending regular daily consumption of eggs. It has been found that eating egg yolk affects different people, differently i.e., the response to eating whole eggs varies between individuals. One study suggests that in 70% of people, eggs don’t raise cholesterol at all, and in 30%, eggs can raise total and LDL cholesterol. It is recommended that individuals with genetic history of hypercholesterolemia should limit the consumption of egg yolks. Also, it is advisable to eat egg yolks in moderation. So, suppose if you are having two eggs a day, it’s better to eat one whole egg and discard the yolk of the other egg to keep the cholesterol intake in check.
If eggs are dirty, wash them to remove the dirt
Eggs become porous when washed, hence never wash eggs. Also, due to washing, Salmonella (a kind of bacteria that causes food borne infection) can move into the inside of the egg through pores in the shell, increasing the risk of infection.
Eggs remain fresh if stored at room temperature and need not be refrigerated
Refrigerating eggs keeps them fresh for longer duration as compared to storing them at room temperature and also minimises the risk of any bacterial growth.
Raw eggs are better than cooked eggs and aids recovery from any disease
Never give raw eggs to anyone including pregnant woman, infants or older people as eating raw eggs enhances the risk of Salmonella infection. It should never be given in raw form to those who are seriously ill, especially when they are sick. It is preferably better to consume cooked eggs in which egg white is firm and yolk is completely thickened. Cooking eggs does not reduce the protein content or nutrients present in them to an unavailable form.

If the egg floats, it indicates that it is a stale/ rotten egg. The egg might float beacause of its weak shell and fine cracks.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Apart from your own home, which place do you eat most frequently on a daily basis? If you think about it, it is likely to be your office, college or an institution that you visit regularly. In today’s fast-paced environment, a large number of working professionals and students are spending the majority of their time at the workplace or college campus. The long working hours, classes or client meetings and short deadlines are only increasing the time spent at these places with little time left for eating healthy or exercising. Hospitals and call centers have workers who spend entire days and even nights working, often at the cost of their health. When we are at work, we are not always mindful of what we eat or drink, often resorting to unhealthy food, drinking excessive tea or coffee or even skipping meals altogether.
Shri Arun Singhal, CEO, FSSAI
In addition to this, safe and healthy options are often not available at most workplaces, leaving no choice but to rely upon what is available to satisfy one’s hunger. Hence, there is a need to ensure that the food we eat at campuses is safe and healthy, given that diet related diseases such as obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and heart diseases are rising at an alarming rate.
To address these concerns and support campuses for ensuring availability of safe, healthy and sustainable diets for their employees, students, patients, inmates, etc., the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has introduced a nation-wide programme called the ‘Eat Right Campus’ (ERC). This initiative has been launched with two objectives, one is to create an environment of safe and healthy food habits for people in various campuses through compliance to a set of well-defined parameters; and continuously reiterating the message of “mindful eating habits’ through awareness activities within the campus premises for continuous behavioural change.
Under this initiative, benchmarks have been created on four different parameters based on which campuses are evaluated and certified as ‘Eat Right Campus’. These parameters include food safety measures, steps to ensure provision of healthy and environmentally sustainable food and building awareness among individuals in the campus to make the right food choices.
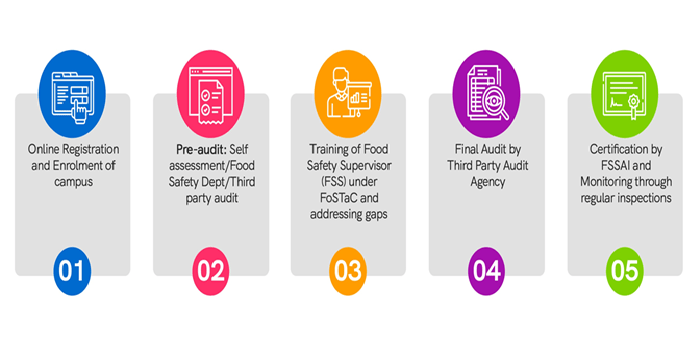
A detailed checklist has been created based on the above four parameters, outlining the best practices to be followed by the food handlers within the campuses. This goes beyond the mandatory requirement of licensing and registration of food service providers within the campuses. The certification is a powerful tool that ensures that food cooked/ handled/ served and stored in the campuses is safe and hygienic. Further, it ensures that food vendors comply with food safety and hygiene standards as per Schedule 4 of the Food Safety and Standards (FSS) Act, 2006. Additionally, the third party audit/ hygiene rating audit of the campus kitchen provides a sense of recognition to the campus, thereby reducing the chances of frequent inspection visits by the food safety department in that area.
Eat Right Campus recognizes the efforts of a campus towards ensuring the health of its people, adds prestige and brand value to its name and inspire others to adopt similar best practices. In particular, it provides a unique opportunity to workplaces to showcase their efforts around employee health and wellbeing. This serves as a key incentive to attract new talent and top performers, thereby boosting high quality recruitment and employee performance. Investing in the health and wellbeing of employees also reduces absenteeism and healthcare costs and ultimately serves to build the reputation of the organization. Many workplaces strive to acquire a high rank in global workplace related ratings/indices. The ERC certification similarly aims to create a sense of competition among campuses across the country towards raising the standards of food safety, nutrition and food sustainability.
With as many as 1346 certified campuses now, this initiative is targeting varied sectors like government organisations, private workplaces, colleges/ universities, tea estates, etc. Recently, a wide range of Government bodies like Anganwadi Centres, Police stations, Jails, Legislative Assembly, Delhi, etc. are covered under the ambit of Eat Right Campus initiative. As this initiative grows to include all campuses in the country, it will contribute to the productivity and economic growth of the country while also safeguarding people’s health.
FSSAI is following a holistic approach by engaging with various institutions of national importance, government colleges, universities, IITs, IIMs, hospitals, and Central government ministries, to enrol them into the programme. Additionally, the Food Authority is working with various industry associations to enrol their member companies under this programme. Similarly, food service establishments like hotels (with a separate staff canteen/ kitchen) are being sensitized to join this initiative and contribute to the productivity and economic growth of our country while also safeguarding people’s health.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.


Shri Arun Singhal, CEO, FSSAI
The Eat Right Challenge was envisioned as a competition among districts and cities to recognize their efforts in adopting and scaling up various initiatives under Eat Right India. Further, it was meant to motivate States/UTs to improve performance and encourage others to join.
Salient Features
The Eat Right India Movement is working on three key themes through a graded “Food Systems Approach” (FSA) to address these issues in a holistic manner by building on the collective action of all stakeholders – consumers, food businesses, community organizations, experts, professionals, and the government. Multiple actions, not only on the supply-side, but also on the demand-side are needed. Therefore, various actionables under the Challenge have been categorized under four sectors:
The Eat Right Challenge for Cities and Districts received participation from 188 cities and districts and 75 have been declared as winners based on their performance across five broad parameters. Grant of Rs. 5, 00,000/- (Rupees Five Lakh Only) to each district/city was provided for undertaking various Eat Right India initiatives. During the Challenge, participating cities and districts had taken various efforts to improve the food environment in their respective areas. The top 10 districts in order of their ranks in top 75 are Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh), Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh), Vadodara (Gujarat), Ujjain (Madhya Pradesh), Thiruvallur (Tamil Nadu), Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh), Kancheepuram (Tamil Nadu), Salem (Tamil Nadu) and Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh).
Further, looking at the overwhelming response from participating districts in Phase I, the Phase II of the Eat Right Challenge for Districts has also been initiated. The Eat Right Challenge for Districts (Phase II) is envisioned as a competition among districts to recognize their efforts in adopting and scaling up various initiatives under Eat Right India. Further, it is meant to motivate States to develop a food strategy that supports a healthy, safe, and sustainable food environment, through participating districts.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.


Chocolates are either critiqued to have negative impact on health or are portrayed by the marketers to have health benefits especially dark chocolates. The truth is that the composition of every chocolate is different from the other one, and this along with the amount of chocolate plays a role in determining if it’s healthy for you or not. In this article, we attempt to list out some factors to understand about this in detail.
Richa Pande
Chocolate is made from cacao beans also known as cocoa beans. The beans are roasted and pressed to release the fat known as Theobroma oil or cocoa butter. The solids are separated and made into cocoa powder. Both cocoa butter and cocoa powder/ nibs are known to have a range of health benefits. For instance, cocoa butter is rich in vitamin E, polyphenols, and a combination of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Cocoa powder too is rich in polyphenols which have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Flavanols in cocoa powder have been proven to improve blood flow to brain tissues, and thus could be helpful prevention of age-related brain degeneration, such as in Alzheimer’s disease. Evidence also suggest that eating flavanol-rich dark chocolate improves insulin sensitivity, has cancer protective impacts, and is good for skin health. Consuming chocolate have also been interlinked with release of endorphins in our body which are help relieve pain, reduce stress and improve your sense of well-being.
These two cocoa components (both cocoa butter and cocoa nibs/powder) are mixed with several other ingredients and different chocolate formulation are prepared. These are some of the common types available in the market-
| Per 100 g | Calories | Total Fats | Saturated fats | Added Sugar | Protein | Ingredients |
|
Brand 1 Milk Chocolate |
545 Kcal | 31.4 | 19 g | 43 g | 8.2 g | Sugar, Cocoa Butter, Milk Solids, Cocoa Solids, Permitted Emulsifiers (E322, E476). Contains Added Flavours (Artificial Flavouring Substances – Vanilla, Cocoa And Condensed Milk). |
|
Brand 2 Milk Chocolate |
530kcal | 30.5g | 18.5g | 56.0g | 7.5g | Sugar, Milk Solids (22%), Cocoa Butter, Cocoa Solids, Emulsifiers (442, 476). CONTAINS ADDED FLAVOUR (NATURAL, NATURE IDENTICAL AND ARTIFICIAL (ETHYL VANILLIN) FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES). Allergen Information: Contains Milk, manufactured on equipment that also processes products containing tree nuts and wheat. |
|
Brand 1 Dark Chocolate 99 % Cocoa |
587 Kcal | 42.3 | 26 g | 0g | 15.1 | Cocoa Solids, Permitted Emulsifiers (E322, E476) |
|
Brand 2 Dark Chocolate 55 % Cocoa |
557 Kcal | 33.7 g | 20g | 43g | 6g | Sugar, Cocoa Solids, Cocoa Butter, Permitted Emulsifiers (E322, E476). Contains Added Flavours (Artificial Flavouring Substances – Cocoa And Vanilla). |
|
Brand 1 Sugar free Chocolate (55% COCOA) |
475 Kcal | 33.7 g | 20g | 0g | 6g | Maltitol, Cocoa Solids, Cocoa Butter, Permitted Emulsifiers (E322, E476). Contains Added Flavours (Artificial Flavouring Substances – Cocoa And Vanilla). |
It is important that most of the negative impacts attributed to chocolate is because of its high sugar content such as acne, diabetes, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, heart disease, etc. Additionally, chocolates decrease oesophageal sphincter pressure which causes acid reflux and heartburn. It is always recommended to pick a chocolate that has low sugar content, and high amounts of cocoa in it. Always pick chocolates after thoroughly going through the ingredient list and the nutritive values.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.