No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

The consumer movement is an organised social movement that promotes consumer protection and is often led by consumer organisations. It argues for consumer rights, particularly when those rights are actively violated by the activities of corporations, governments, and other organisations that offer customers with goods and services. Consumer movements frequently push for higher health and safety standards, truthful product information in advertising, and consumer representation in legislative bodies.
Bhamy V. Shenoy
Ralph Nader is widely regarded as the founder of the current consumer movement in most parts of the world. In India, however, we do not have a single such towering leader. Manubhai Shah, the founder of the Consumer Education and Research Centre (1978), and H. D. Shourie, the founder of Common Cause (1980) are both deserving of such a high honour. Manubhai Shah focused mostly on assisting individuals with personal problems or identifying consumer issues. Shourie’s initiatives aimed to effect systemic change through PILs filed before the Supreme Court.
In Karnataka some of the pioneers of the consumer movement were Jajie Mandanna, the founder of Karnataka Consumers Services Society (1974), Dr. K P S Kamath, the founder of Udupi Balakedarara Vedike (1980), and Prof Narayan Rao in Udupi. There were some well-known NGOs who followed the pioneers at the national level: Sriram Khanna of Consumer Voice in Delhi (1983), S R Desikan of Consumer Association of India in Chennai (1983), and Pradeep Mehta of Consumer Unity and Trust in Kolkata (1984). But before the mid-80s, there were not many NGOs in the consumer protection movement. However, special mention must be made of an individual activist M. R. Pai of free enterprise in the 80s. He concentrated on fighting for consumer-friendly services from monopolies like Indian Airlines, Indian Nationalized Banks, and Indian Telephones.
The adoption of the Consumer Protection Act on December 24, 1986 (COPRA) was a major impetus for the Modern Consumer Movement in India. Because of such a revolutionary Act, India observes December 24 as National Consumer Day. However, even after ten years, there were less than 800 NGOs, most of which had minimal budgets and relied on government handouts. There are currently roughly 2000 NGOs, the majority of which exist simply on paper.
It is paradoxical that in the US, President Kennedy has been credited as launching the Consumer Movement on March 15, 1962 by declaring four consumer rights – right to Safety, right to Information, right to be Heard, and right to Choose. In 1982, Consumer International, which has membership of 250 consumer groups, decided to celebrate March 15 as World Consumers Rights Day.
Consumers in the US were protected through competition and strong laws preventing unfair trade practices. But in India where consumers were taken for a ride in the absence of competition, we had to wait till 1986 to get the progressive Consumer Protection Act. To add to the woes of Indian consumers, our court system is notoriously slow in solving disputes where justice was often delayed and thus denied by endless adjournments. Thus, COPRA was a saviour. Unfortunately, it did not last long. The main ideals of COPRA were to give speedy (within 90 days) and summary justice without involving lawyers. Unfortunately, today these consumer redressal commissions have become “civil courts” where adjournments are normal, lawyers are never present and summary trials are never held.
But none of the consumer NGOs was big enough or had enough expertise to bring about systemic changes to promote competition. It was the time when one had to wait for months, if not years to buy scooters/motor bikes, get telephone connection, procure LPG, etc. For buyers of cars, choice was limited to three brands. It was only after 1991 when economy was liberalized, consumers were able to have their choice while buying cars and two wheelers and too without waiting. Air travel became easier and cheaper with the entry of several private airlines, and much later, we also had the choice of phone connections when mobile phones became available.
However, the nascent consumer movement did not realize that the best weapon to help consumers is competition and not a plethora of laws and regulations. For that matter, even now most NGOs concentrate on helping consumers through COPRA, which was significantly improved in 2019. New features of the Consumer Protection Act were mediation, imposing fines on celebrities for misleading and false ads, bringing online trading under the preview of the act, filing cases online, product liabilities, setting up of a Consumer Protection Authority, etc.
Nevertheless, even the best act cannot help the consumers if those in authority fail to implement it in true spirit and have empathy for long suffering consumers. Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) Act is one such act. Because of the failure to implement it, food adulteration is rampant (as much as 20%), affecting the health of millions. NGOs need to work in not only helping consumers to use COPRA but also to put pressure on the government to enforce the implementation of the Acts in true spirit. Often the laws like FSSAI are used as weapons of corruption rather than to help citizens.
Soon after the passage of COPRA, consumer NGOs organized national level annual meetings to discuss strategies to strengthen consumer movement. First such meeting was held in Kochi (1990) followed by Delhi (1991 and 1993), Kolkata (1992), and Hyderabad (1995). Efforts to form a pan-India umbrella organization did materialize in 1991 to form Confederation of Indian Consumer Organizations. But it lasted only for a few years. Well-established leaders like Manubhai Shah, and H. D. Shourie kept away from such meetings. Once the initial momentum of COPRA started to wane and consumer redressal commissions became replica of civil courts, the decline of Indian consumer movement began.
While we can find fault with the NGO leaders for their lack of vision and leadership qualities, main culprits are the consumers themselves. We the citizens, especially the literate ones, do not take responsibility while living in a democracy. Our duty is to take an active part in the democratic process of electing honest, dedicated, and competent leaders by casting our votes. Only then does a Consumer become King in the private sector, and citizens will be treated as masters while seeking services from servants of the government. Unfortunately, today, we are neither “Kings” nor “Masters” because of our failure to fulfil our duties s citizens.
Even the basic responsibility of getting a receipt while buying goods or services is not complied with by most consumers. When given a chance to save taxes, we are tempted not to demand receipts. We do not realize that we then lose our rights as consumers to use the Consumer Protection Act however progressive it may be. Even when we are cheated, how often do we protest?
Though we know very well that only when we are united and have a strong organization (think of labour unions fighting for members’ rights), we can fight for our consumer rights against the more powerful profit-driven private enterprises or corruption-ridden, inefficient government bureaucracy. Still, we do not even become a member of credible NGOs to support activists which are public-spirited. On the other hand, some try to find faults with the activists or criticize them for not taking up what they think are more pressing problems, or they completely ignore them just as they ignore taking part in democratic processes.
To revitalize the consumer movement, we need just two simple strategies – to take active part in the democratic process of electing the most suitable candidates, and second, to support and take active part in the consumer movement. The million-dollar question is how to implement these strategies.
After examining the growth and fall of the consumer movement, as well as proposals for revitalization, it may be good to conclude by relating the experience of Mysuru Grahakara Parishat (MGP). Even at the risk of being accused of blowing my own horn, I’d like to explain briefly, if subjectively, the successes and shortcomings of MGP, which I founded in 1989.
There has not been a single issue affecting Mysuru that MGP has not attempted to resolve in its 33 years of existence. Apart from assisting thousands of individual citizens in resolving their problems, MGP attempted to effect systemic changes in institutions in order to minimise corruption and improve the standard of living for all customers.
They are:
Despite our mixed success, we have considerable visibility in the city today. Some commissioners’ have complimented that every city should have an NGO like MGP, which is beneficial to authorities too. However, despite MGP’s initial objective of obtaining 10,000 members in the first five years, we have never surpassed 1000. However, MGP has succeeded in establishing a strong platform for a number of activists to serve Mysuru. This was accomplished entirely via the efforts of volunteers, with no government funding.

Ralph Nader

Jajie Mandanna

H D Shourie

M R Pai

Manubhai Shah

K P S Kamath



The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
There is no particular date on which we launched VOICE in April 1983 at the Delhi School of Economics campus at Delhi University. There was no launch ceremony or event. It was born out of the drafting of a complaint by VOICE signed by me and about 30 of my students. One student took it around and got the signatures. I had been drafting the complaint based on invoices of purchase of 20 inches Colour TVs which were being sold in retail much above the retail price of ₹7500 in the import undertaking given to the Government on import of Kits to assemble the CTVs.
We had been collecting the invoices over previous few weeks. I remember that the complaint was ready to be filed at MRTPC (Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Commission) around Baisakhi, 13 April 1983. That is the reason I regard Baisakhi of 1983 as founding day of VOICE.
Prior to this I had asked my students in a class on ‘branding’ what name would they give to a Consumer association to be formed to fight for consumer rights? I got about 40 slips. One of these slips had the name – Voluntary organisation in Interest of Consumer Education (VOICE) . I instantly picked this name. Soon a letterhead was created and the complaint to MRTPC was typed on it.
It’s been 40 years since. The Delhi University routine was quite different at Delhi School of Economics where I had been appointed as a Lecturer in Commerce in 1982. I had been working as a Lecturer in Commerce at Bhagat Singh College then located in Govindpuri from 1977 where my focus was on completing my PhD which was awarded in 1980. An 18 hour/ week teaching schedule and PhD research work kept me busy at the college. However, with a shift to the main University campus my teaching load was relatively lesser and gave me relatively more time to read and write. My interest in consumer movement was kindled reading a marketing text book by Stanton which I was using to teach a Marketing paper to M.Com students as a part of my job. It traced the impact of the US Consumer Movement on the US consumer and retail markets and B2C corporations and brands. It had led me to ask the question ‘Why can’t we have a similar movement in India?’ I had discovered a provision in the MRTP Act, 1969 which allowed an unincorporated Voluntary Consumer Association to file a complaint against businesses for restrictive trade practices. I had drafted the complaint based on over charging consumers on sale of CTVs in violation of undertakings given by heading brands like Weston , Dyanora, Dynavision , BPL etc at time of import of kits. Most of this information had been culled out of un-stared questions drafted by me and filed by some BJP MPs in Lok Sabha with whom I had close links in those days due to my past association with ABVP.
This complaint was filed shortly thereafter at the MRTPC located at Travancore House. An investigation ensued. MRTPC issued notice to Bharat TV and 43 other assemblers and dealers named in preliminary investigation report prepared by DG (I&R) in early 1984. This case number 183 of 1984 VOICE vs Bharat TV & 43 others kept me busy for more than a decade. We won the case over a decade later but that is another story.
Prof Shri Ram Khanna
Chief Editor
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Buttermilk is an excellent summer beverage that is not only refreshing and delicious, but also good for your health. Buttermilk has numerous benefits, including being low in calories and fat, high in protein and calcium, and containing probiotics which can help improve digestive health. It’s also a great source of potassium, magnesium, and other essential vitamins. Not to mention that it’s an incredibly versatile drink that can be used in a variety of recipes. Whether you’re looking for a light summer refresher or something a little more indulgent, buttermilk makes an excellent choice. In this article, we have summarized some of the health benefits of buttermilk, how you can add healthy ingredients to make this drink more nutritious, and recipes to help you incorporate buttermilk into your daily diet.
Richa Pande
Buttermilk, also known as chaas in some parts of India, is a refreshing drink made by churning yogurt and water. It is a fermented dairy beverage and is slightly sour in taste. Its cooling nature makes it a great thirst quencher on a hot summer day. Not only is buttermilk delicious, but it is also incredibly healthy.
Buttermilk has numerous health benefits that range from promoting gut health to strengthening bones and teeth. It also helps to keep dehydration at bay and even relieves acidity. Furthermore, it has low calorie content which makes it an ideal choice for those looking to lose weight while still enjoying the benefits of consuming dairy products. Compared to other dairy products, its fat content is also low. It also benefits your oral health. Calcium from fermented dairy foods has been linked to a significant reduction in periodontitis.
Due to its nutritive properties, it can be effective in management of elevated blood pressure. Therefore, buttermilk can be considered a nutritious and delicious beverage that can have great benefits for our overall health. Buttermilk can do wonders for your skin too. It is a nutrient-rich drink which is packed with vitamins, minerals, proteins and probiotics that can improve the look and feel of your skin. Not only does it provide essential nutrients to keep your body healthy, but it also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties which can help reduce wrinkles and other signs of aging. Furthermore, regular consumption of buttermilk can help protect your skin from sun damage, acne breakouts, dryness and other skin problems.
Buttermilk can be easily prepared at home by adding water to curd and then blending them. You can also prepare buttermilk by adding vinegar /lime juice to regular milk.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Every year we observe March 8 as International Women’s Day. According to the Unite Nations, the purpose of this day is to uphold women’s achievements, recognize challenges, and focus greater attention on women’s rights and gender equality. The state of women’s health and nutrition is critical to their overall well-being. Adequate nutritional status of women significantly impacts their work capacity and the health of their children. Eating a well-balanced diet and practicing good nutritional habits can aid in the prevention of several ailments, and thus help in maintenance of good health. In this article, we discuss some of the major nutritional disorders prevalent among Indian women, nutritional needs of women during different life stages, and some tips to address these concerns.
Richa Pande
According to the NFHS 5 data, more than 50 % Indian women and adolescent girls are anaemic. There’s high prevalence of malnutrition concerns like underweight and overweight/obesity at the same time. Additionally, the prevalence on non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like hypertension, diabetes, cancer, heart disease, arthritis, and osteoporosis among Indian women.
They also struggle with micronutrient deficiencies. The above data gives us an insight about the nutritional status of Indian women.
The above data gives us an insight about the nutritional status of Indian women. Now lets us try to understand the reasons behind it. Women are more likely than men to experience nutritional deficiencies due to a variety of factors, including their reproductive biology, low social status, poverty, and lack of education.
Women have different nutritional needs at different stages of life. Women go through several hormonal changes throughout their lives, making certain nutrients essential at different stages for their healthy development and overall well-being.
During adolescence a girl goes through many physical and hormonal changes coupled with increased growth rate, hence nutritious food is essential for her growth and development. Her diet must include all essential macro and micronutrients with an emphasis on adequate consumption of Protein, Calcium, and Iron. Consumption of junk food should be limited. It’s important to practice healthy eating habits during this stage as these will be carried on into later stages of life.
Post adolescence, women undergo a transformative stage as well as these are the years when they pursue higher education, career interests, get married, and plan a family. It’s natural to get stressed during this stage but it’s important to deliberately make good health choices such as staying physically active, taking care of your mental health, avoiding emotional eating, etc. It’s important to have enough amounts of Protein, Iron, Calcium, Vitamin D, Omega -3 fats, and Vitamin B12.
It’s crucial for a woman to have a good nutritional status if she is planning to get pregnant. Women diagnosed with PCOD, thyroid, or anaemia must take special care of their health especially if they are planning to get pregnant. Underweight and overweight women should also focus on weight management before conceiving a child. You can seek a nutritionist/ health practitioner’s advice to manage your diet if you are planning to get pregnant. It’s important to understand that pregnancy can affect your mental health. Also, you can deal with post-partum depression, thus it is advisable to stay educated about mental health and take necessary precautions before pregnancy itself. Know that to deal with the changes during this stage, you need a strong body and mind, which can only be obtained by adopting a healthy eating style, sufficient physical activity, and adequate rest.
During pregnancy, it’s important to seek the advice of a health practitioner and follow it. Take proper rest and adequate sleep. Have foods rich in folic acid, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Calcium, Omega-3 fats and Iron. If you face any discomfort, discuss it with your healthcare provider. It’s also important to educate yourself about feeding your child in advance. It’s also important to have knowledge about your nutritional needs when you are feeding your child. You can discuss this with a nutritionist or a dietitian and can further self-educate yourself about it via literature recommended by your health practitioner. Note that along with the nutrients, your fluid intake will play an important role in managing the feeding experience.
It’s important to take care of your health throughout your life but special emphasis must be put on it when you are in your late thirties and early forties. Educating yourself about perimenopause, and menopause is a good idea. Women start perimenopause at different ages. During this stage, you might notice some irregularity in your periods. You are diagnosed to have menopause once you’ve gone through 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. It’s important to have regular health check-ups during this stage, eating healthy, staying physically active, and taking proper rest and adequate sleep. Practicing yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises can be soothing. It’s vital to have foods rich in Calcium, Folic acid, Vitamin B12, Vitamin C, and Fibre. It’s important to note that post menopause, your body requirement of Iron decreases. If you were taking Iron supplements before menopause, consult your health practitioner for an adjusted dose for during perimenopause and post-menopause.
|
Dietary sources of some micronutrients crucial for women’s health |
|
|
Calcium |
Cereals and legumes like ragi, bengal gram, horse gram, rajma and soyabean). Green leafy vegetables like amaranth, cauliflower greens, curry leaves, knol-khol leave, agathi leaves, Colocasia leaves. Nuts and oilseeds like almonds, sesame seeds, tahini seeds, etc. Dairy products like milk, curd, yogurt, buttermilk, cheese, etc. |
|
Iron |
Green leafy vegetables such as amaranth, spinach, bengal gram leaves, cauliflower greens and radish leaves. Organ meats, poultry, and seafood. Oilseeds like pumpkin seeds, flax seeds, and sunflower seeds. Fortified Salt. Eating iron rich foods with foods rich in Vitamin C improves the absorption of iron. |
|
Vitamin B9/ Folate/ Folic Acid |
Vegetables such as broccoli, amaranth, beets, peas, kale, spinach, etc. Pulses like chickpeas, bengal gram, black gram, green gram, and red gram. Oil seeds like peanuts, sesame seeds and sunflower seeds. Eggs are also a good source of vitamin B9.Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruit, lemons, and limes are rich in folic acid. Papayas, Bananas, Avocados ARE ALSO RICH IN FOLATE. |
|
Vitamin C |
amla, guava, kiwis, lemons, oranges, papaya, strawberries, tomatoes , |
|
Vitamin D |
egg yolk, salmon, tuna, cod liver oil, sardines, mushroom, Vitamin D fortified foods |
It’s time for women to prioritise their own nutritional and health needs because taking care of ourselves comes before taking care of others. Women frequently disregard these needs. They must also ask for assistance when they need it rather than struggling silently and letting it affect their wellbeing.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Makhana, also known as Foxnut, is a widely consumed snack during fasting in India. It is becoming a popular snack among health-conscious consumers due to its healthier nutrient. Makhana is mixed with different seasoning and flavouring substances, and a range of ready -to-eat Makhana snack packs are available in the market. In this article, we discuss the nutrient profile of foxnut, spell out its health benefits, share some recipes that are easy to prepare at home, and give some tips on how to pick a healthier version of ready-to-eat makhana snack from market.
Richa Pande
Makhana is the edible seed of the gorgon plant, a species of water lily, and thus it is also called the Lotus Seed. Traditionally, the seed is roasted or fried, and is mixed with oils and herbs and eaten during fasting observed in India during Navratri and in the month of Sawan.
Makhana has a healthy nutrient profile. 100 g of makhana provides about 347 calories of energy, contains about 9.7 g of protein, and has 14.5 g of fibre. It is also a good source of micronutrients such as- potassium, magnesium, iron, and calcium. These micronutrients play an important role in metabolic activities thus promoting our wellbeing. Makhana is also rich in natural antioxidants such as Gallic acid, kaempferol and chlorogenic acid that have many health benefits.
Makhana is the edible seed of the gorgon plant, a species of water lily, and thus it is also called the Lotus Seed. Traditionally, the seed is roasted or fried, and is mixed with oils and herbs and eaten during fasting observed in India during Navratri and in the month of Sawan.
Makhana has a healthy nutrient profile. 100 g of makhana provides about 347 calories of energy, contains about 9.7 g of protein, and has 14.5 g of fibre. It is also a good source of micronutrients such as- potassium, magnesium, iron, and calcium. These micronutrients play an important role in metabolic activities thus promoting our wellbeing. Makhana is also rich in natural antioxidants such as Gallic acid, kaempferol and chlorogenic acid that have many health benefits.

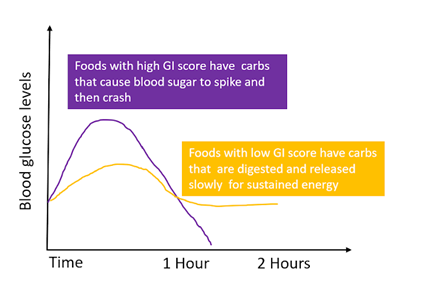
The glycaemic index score of fox nuts is under 55, and thus makhana can be classified as low GI food. Low GI foods are the food items that contain carbohydrates which are digested slowly in the body. Eating them leads to a gradual and comparatively low rise in the blood glucose and insulin levels. This also means that these foods can help you keep feeling full for a longer duration. Therefore, these food items are considered good for health, and are specifically recommended to individuals who have diabetes.
As fox nut is rich in antioxidants, it is also considered good for skin health, heart health, and could be helpful in prevention and management of chronic inflammation. It is a good snack for individuals with rheumatic arthritis. Its fibre content makes it good for your digestive health as well.
Fox nut is a great snack for individuals with wheat allergy or gluten intolerance. But some ready-to-eat makhana packs may have seasonings that might contain ingredients like wheat flour. Thus, it is very important to check labels, and avoid picking packs with such ingredients. Look for packets that have ‘Gluten-Free’ claim on them.
Makhana is high in magnesium, calcium and potassium and low in sodium. Thus, it is a good snack for people who have hypertension. Some ready-to-eat makhana packs might have added salt and thus you must go through the food labels to avoid picking such packs. As makhana is rich in calcium, it is also good for your bone and teeth health.
Makhana is also a good source of selenium which is known to be effective in prevention and management of thyroid disorders. Due to its healthier nutrient profile, it also makes an excellent snack for pregnant women, and individuals aiming for weight loss.
Check the ingredient list, and nutritive value table before choosing a snack
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.