World Consumer Rights Day 2020
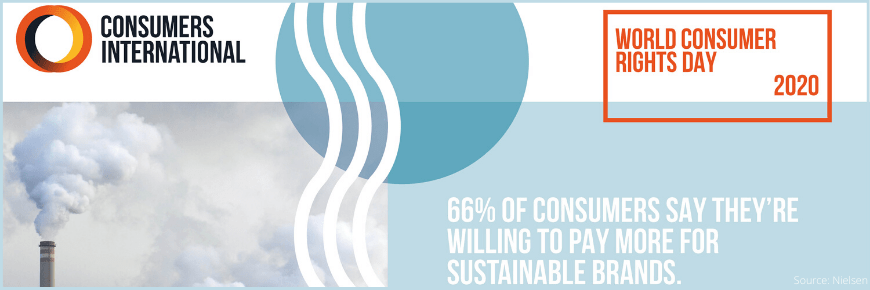
Climate change is affecting millions of people the world over. This problem should be urgently addressed by global leaders to avert an environmental breakdown and one of the solutions is sustainable consumption. Consumers have a great role to play in this and as a recent study shows that 66% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable brands. In another report by IKEA, it shows that global population is becoming more informed and anxious about climate change. But though the concern is there, consumers at large feel that not enough action is being taken. A recent survey found 37% don’t know how they can help tackle climate change and 59% feel they do not get enough support from governments, and 51% from business.
THEME OF WORLD CONSUMER RIGHTS DAY 2020
Keeping the urgent need to take drastic action to save our environment and prevent biodiversity loss, World Consumer Rights Day 2020 is being celebrated with the theme ‘The Sustainable Consumer’. World Consumer Rights Day is celebrated on 15th March every year, where consumer organizations all over the world come together to highlight and raise awareness on issues concerning consumers.
Consumer VOICE too is committed to make the world a better place for consumers from every aspect including protecting it from climate change. Consumer VOICE has chosen E waste management as its theme.
WHAT IS SUSTAINABLE CONSUMPTION
Sustainable consumption is the consumption of goods and services that have minimal impact upon the environment, are socially equitable and economically viable whilst meeting the basic needs of humans, worldwide. Sustainable consumption targets everyone, across all sectors and all nations, from the individual to governments and multinational conglomerates.
We as consumers have a task in hand if we want to move towards sustainable consumption.Around the world, nearly one million plastic bottles are sold every minute, and five trillion pieces of plastic are floating in our oceans.We buy over 80 billion new clothing items a year, and consume 3.9 billion tonnes of food – one-third of which is lost or wasted.
It is time for us to act for our future generations. Climate change is the worst effect of unsustainable consumption. The decade of the 2020s is our last chance to limit global warming to 1.5c since pre-industrial times, in line with the Paris Agreement and to reverse the current trend of wide-scale biodiversity loss.
WHAT CAN BE DONE?
Unsustainable Packaging
What we are shopping either online or offline we tend to hoard unnecessary packaging. Among all packaging food packaging waste equals to almost one third of all trash. Some medicines have two to three layers of plastic packaging too. It is time to demand for either recyclable or reusable packaging.
Unsustainable transportation
The automobile sector adds to the global carbon footprint in a big way. Polluted vehicles, rampant use of personal transport in place of public transport leads to release of carbon monoxide. Ride sharing and use of e-vehicles will help consumers work towards a more sustainable consumption.
Unsustainable Electronic Goods Consumption
Electronic goods are being bought and consumed at a fast rate but its disposal is equally quick. This leads to e-waste which adds toxins to the already polluted environment of ours. We need to guard ourselves against decreasing product lifetime? Though most consumers know some products are designed to die after a certain point, the thought is less acceptable.
Consumer VOICE has therefore decided to work towards controlling e-waste, an important part of sustainable consumer.
WHAT IS E WASTE?

Electronic waste, abbreviated as ‘e-waste’ is a term used to describe old, end-of-life electronic appliances such as computers, laptops, TVs, radios, refrigerators among others which have been discarded by users.
E-waste is a cocktail of toxins like mercury, lead, cadmium, arsenic, and beryllium or brominated flame retardants that are hazardous to human health and the environment if not recycled using state-of-the art technology. E-waste is not just a problem of waste quantity or volumes. The concern is compounded because of the presence of toxic materials like lead, mercury, cadmium, certain BFRs (brominated flame retardants) and many other chemicals.
With the usage of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) on the rise, the amount of electrical and electronic waste (e-waste) produced each day is equally growing enormously around the globe.
E WASTE IN INDIA
Did you know?
Computer equipments account for almost 70 per cent of e-waste followed by telecommunication equipments -phones (12 per cent), electrical equipment (8 per cent) and medical equipment (7 per cent) with the remaining coming from household e-waste.
- India accounts for roughly 4 per cent of e-waste generated annually.
- Mumbai topped the list as it generated an estimated 1,20,000 tonnes of e-waste annually.
- Delhi and Bengaluru ranked second and third, with 98,000 and 92,000 tonnes of e-waste generation respectively.
- Approximately 70 per cent of heavy metals found in landfills are accounted for by E-waste.
- Since 2018, India generates more than 2 million tonnes of e-waste annually, and also imports huge amounts of e-waste from other countries around the world.
(Source: ASSOCHAM-KPMG study, titled “Electronic Waste Management in India’’)
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO MANAGE E WASTE?
E waste is potentially harmful to the environment and causes hazardous diseases. It affects the air, water and soil too. When improperly disposed of, the heavy metals, plastics and glass in e-waste can pollute the air or seep into waterways. It harms the plants and trees and thus dislodges the ecological balance. In addition to its hazardous components, being processed, e-waste can give rise to a number of toxic by-products likely to affect human health.
E-waste-connected health risks may result from direct contact with harmful materials such as lead, cadmium, chromium, brominated flame retardants or polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), from inhalation of toxic fumes, as well as from accumulation of chemicals in soil, water and food.
Primitive recycling techniques such as burning cables for retaining the inherent copper expose both adult and child workers as well as their families to a range of hazardous substances.
E WASTE DISPOSAL & MANAGEMENT
Managing E-waste is crucial for sustainable development. E waste which is becoming a huge public health issue needs to be addressed immediately. In order to separately collect, effectively treat, and dispose of e-waste, as well as divert it from conventional landfills and open burning, it is essential to integrate the informal sector with the formal sector. The competent authorities in developing and transition countries need to establish mechanisms for handling and treatment of e-waste in a safe and sustainable manner.
Increasing information campaigns, capacity building, and awareness is critical to promote environment friendly e-waste management programmes. Increasing efforts are urgently required on improvement of the current practices such as collection schemes and management practices to reduce the illegal trade of e-waste. Reducing the amount of hazardous substances in e-products will also have a positive effect in dealing with the specific e-waste streams since it will support the prevention process.
ROLE OF CONSUMER VOICE
Consumer VOICE will explore and study the problem on how one can tackle the problem of e-waste. One of the ways is to sensitize children, youth and communities about the perils of e-waste and how they can to tackle it.
Children are one of our main target groups as gadgets and electronic goods are more commonly used by Generation Z. So the best possible way to address the problem is through social media. Consumption of electronic goods in the digital era is maximum by this generation which also results in a heavy amount of e-waste. Consumer VOICE plans regular messaging and interactive sessions which will empower children.
